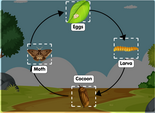
Biology Diagrams: Enhancing Understanding in the World of Life Sciences
Biology diagrams are indispensable tools in the field of life sciences, aiding in the comprehension of intricate biological concepts. They serve as visual aids that simplify complex information, making it easier for students, researchers, and professionals to understand and retain key principles. In this article, we delve into the significance, types, creation process, design tips, applications, and examples of biology diagrams.
Animal cell diagram
Label the diagram of an animal cell game and worksheet for children.
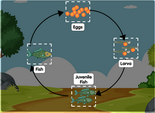
Fish diagram
Label parts of a fish diagram for children. Drag and drop worksheet game online.
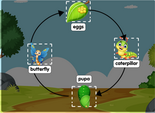
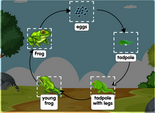
Frog diagram
Frog diagram labelled - interactive online game quiz. Worksheet on frog diagram.
Leaf diagram
Leaf cross section diagram - Label the parts of a leaf with drag and drop.
Lung diagram
Human lungs diagram for children. Learn to label the parts of a human lung.
Plant cell diagrams
Label the parts on a plant cell diagram through an interactive worksheet game.
Skin diagram
Labelled digram of a skin for kids - Online game on labelling skin diagram.
Importance of Biology Diagrams
Understanding Complex Concepts
Biology is a vast and complex field encompassing various disciplines such as genetics, anatomy, and ecology. Diagrams help break down these complex concepts into simpler, digestible components, facilitating better understanding and retention of information.
Visual Aid for Learning
Visual learning is proven to be highly effective, with studies indicating that visuals enhance comprehension and memory retention. Biology diagrams provide a visual representation of biological structures, processes, and relationships, making learning more engaging and accessible.
Types of Biology Diagrams
Cell Diagrams
Cell diagrams illustrate the structure and function of cells, including organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. These diagrams are fundamental in biology education and research, helping elucidate cellular processes like mitosis, meiosis, and cellular respiration.
Molecular Diagrams
Molecular diagrams depict the structure of molecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, and lipids. They showcase the arrangement of atoms and bonds within molecules, facilitating the understanding of biochemical processes like transcription, translation, and protein synthesis.
Organism Diagrams
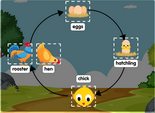
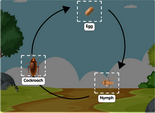
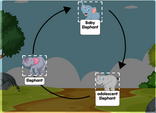
Organism diagrams represent the anatomy, physiology, and ecological relationships of organisms ranging from single-celled microorganisms to complex multicellular organisms. These diagrams aid in studying topics such as anatomy, physiology, taxonomy, and ecology.
How to Create Biology Diagrams
Creating effective biology diagrams requires the utilization of appropriate tools and a systematic approach.
Tools and Software
Various software tools are available for creating biology diagrams, including graphic design software like Adobe Illustrator, diagramming software like Lucidchart, and specialized biology software like Biology Workbench and BioRender.
Step-by-Step Process
The process of creating biology diagrams involves:
- Identifying the concept or structure to be illustrated.
- Researching and gathering relevant information and reference materials.
- Sketching a rough draft of the diagram layout.
- Digitally creating the diagram using chosen software, incorporating labels, annotations, and visual elements.
- Reviewing and refining the diagram for accuracy and clarity.
Tips for Designing Effective Biology Diagrams
Clarity and Simplicity
Ensure that the diagram is clear and easy to understand, avoiding clutter and unnecessary complexity. Simplify complex structures and processes into easily discernible components.
Correct Labeling
Accurate labeling is crucial for conveying information effectively. Label each component of the diagram clearly and appropriately, using standardized biological terminology.
Use of Colors and Visuals
Incorporate colors, shapes, and visuals to enhance the visual appeal and clarity of the diagram. Use color coding to differentiate between different structures or components, aiding in comprehension.
Applications of Biology Diagrams
Education
Biology diagrams are extensively used in educational settings, including classrooms, textbooks, and online learning platforms. They play a vital role in teaching and learning biological concepts at various levels, from elementary school to university.
Research
In research, biology diagrams are employed to illustrate experimental procedures, data interpretation, and research findings. They help researchers communicate their work effectively and enhance the understanding of complex scientific concepts within the scientific community.
Medical Field
In the medical field, biology diagrams are utilized for educational purposes, patient communication, and medical illustration. They aid healthcare professionals in understanding anatomy, physiology, and medical procedures, contributing to improved patient care and treatment outcomes.
Examples of Well-Designed Biology Diagrams
- The cell cycle diagram, illustrating the stages of cell division.
- The DNA replication diagram, depicting the process of DNA synthesis.
- The ecosystem diagram, illustrating the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem.
Conclusion
Biology diagrams are invaluable tools that facilitate understanding, learning, and communication in the field of life sciences. By incorporating clear, well-designed diagrams into educational materials, research papers, and presentations, we can enhance the comprehension and dissemination of biological knowledge.
FAQs
-
Why are biology diagrams important? Biology diagrams simplify complex concepts, making them easier to understand and remember.
-
What tools can I use to create biology diagrams? Various software tools like Adobe Illustrator, Lucidchart, and Biology Workbench are available for creating biology diagrams.
-
How can I ensure the accuracy of my biology diagram? Thorough research and review of reference materials are essential to ensure the accuracy of biology diagrams.
-
What are some common types of biology diagrams? Common types include cell diagrams, molecular diagrams, and organism diagrams.
-
How are biology diagrams used in the medical field? In the medical field, biology diagrams are utilized for educational purposes, patient communication, and medical illustration.