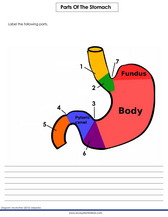
Parts of the stomach labeling quiz
Parts of the stomach labeling quiz online. This is a bilogy quiz online for children in 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th grades. Anatomy of the stomach labeling quiz. This quiz contains the diagram of the stomach showing differeng compartments. Students are required to find and match the correct name of each compartment. This is an interactive online test which parents and teachers can use to supplement their kid's regular course. Below is a worksheet pdf on labeling a stomach diagram.
The Parts Of The Stomach And Their Functions
The stomach is a muscular organ located in the upper abdomen, and it plays a key role in digestion by breaking down food into smaller particles that can be absorbed by the body. The stomach has several parts, each with its own specific function:
-
Cardia: The cardia is the uppermost part of the stomach, which is closest to the esophagus. Its function is to receive food from the esophagus and prevent it from flowing back up.
-
Fundus: The fundus is the upper curved part of the stomach, located above the body. It acts as a storage area for food before it is released into the rest of the stomach for digestion.
-
Body: The body is the largest and main part of the stomach, where the majority of the digestive process occurs. The body mixes and grinds food with stomach acid and digestive enzymes, which helps to break it down into smaller particles.
-
Antrum: The antrum is the lower part of the stomach that connects to the small intestine. Its primary function is to regulate the release of food into the small intestine, ensuring that the digestive process is controlled and efficient.
-
Pylorus: The pylorus is a valve-like muscle that controls the release of food from the stomach into the small intestine. It ensures that the food is properly digested before it enters the small intestine and prevents undigested food from passing through.
Overall, the stomach is an essential part of the digestive system, and each of its parts plays a critical role in breaking down food and preparing it for absorption by the body.
Labels of the Digestive System: Understanding the Anatomy and Functions
The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and structures responsible for breaking down food and absorbing nutrients. The digestive system starts with the mouth and ends with the anus, and includes the following structures:
-
Mouth: The mouth is the beginning of the digestive system. It contains teeth for chewing and breaking down food, saliva to help lubricate and begin the process of digestion, and the tongue to help push food back to the teeth for chewing.
-
Esophagus: The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It uses rhythmic contractions to push food down to the stomach.
-
Stomach: The stomach is a muscular sac that contains acid and digestive enzymes. It mixes food with these enzymes and acid to break it down into a liquid consistency that can be easily absorbed by the small intestine.
-
Small intestine: The small intestine is a long, narrow tube that absorbs most of the nutrients from the broken-down food. It is lined with tiny, finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption.
-
Large intestine: The large intestine is a wider tube that absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining undigested food. It also contains beneficial bacteria that help break down any remaining nutrients.
-
Rectum: The rectum is a short tube that stores feces until it is ready to be eliminated.
-
Anus: The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive system through which feces are eliminated.
In addition to these structures, the digestive system also includes several accessory organs that play a role in digestion:
-
Liver: The liver produces bile, which helps break down fat in the small intestine.
-
Pancreas: The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that are released into the small intestine.
-
Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores and releases bile into the small intestine when needed.
Overall, the digestive system is responsible for breaking down food into its basic components, absorbing those components into the body, and eliminating waste products.
FAQs:
Here's an FAQ section on the human digestive system:
-
What is the primary function of the digestive system? The primary function of the digestive system is to break down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by the body and to eliminate waste products.
-
What are the three main types of nutrients that the digestive system breaks down? The three main types of nutrients that the digestive system breaks down are carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
-
What is the role of enzymes in digestion? Enzymes are molecules that speed up chemical reactions in the body. In digestion, enzymes help break down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
-
What is the role of stomach acid in digestion? Stomach acid helps break down food and kill harmful bacteria that may be present in the food.
-
What is the role of the small intestine in digestion? The small intestine is where most of the nutrients from food are absorbed into the body. The small intestine is lined with tiny, finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption.
-
What is the role of the large intestine in digestion? The large intestine absorbs water and electrolytes from the remaining undigested food. It also contains beneficial bacteria that help break down any remaining nutrients.
-
What is the role of the liver in digestion? The liver produces bile, which helps break down fat in the small intestine.
-
What is the role of the pancreas in digestion? The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that are released into the small intestine.
-
How long does it take for food to travel through the digestive system? The time it takes for food to travel through the digestive system varies depending on the individual and the type of food. On average, it takes between 24 and 72 hours for food to travel from the mouth to the anus.
-
What are some common digestive system disorders? Common digestive system disorders include acid reflux, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and constipation.
Label The Human Digestive System